Describe Three Important Uses for Atp Chemical Transport Mechanical Work
It also supplies energy to the flagella and chromosomes to maintain. Mechanical workATP supplies the energy needed to permit muscles to contract cilia and flagella to beat chromosomes to move and other functions.

Generating Responsive Artificial Cells Using Molecular Download Scientific Diagram
Which of the following does not describe uses for the ATP molecule.
. ATP-Driven Work Cells need energy to grow reproduce and maintain homeostasis but for the energy provided by ATP to be useful it must be coupled with work. In a cell this work takes three main forms chemical work mechanical work and transport work. Your cells perform three main types of work.
To do this it must convert the chemical energy of ATP into mechanical work and ATP hydrolysis may be very tightly coupled to the number and length of. Glutamine synthesis is an example of how ATP hydrolysis is. The energy is released from ATP when the bonds between the phosphate groups are broken down.
The energy is released from ATP when the bonds between the phosphate groups are broken down. Building large molecules such as proteins. Select the most correct statement regarding nucleic acids.
Mechanical work chemical work transport across membranes pigment structure. ATP stands for Adenine Nucleotide which is chemically bound to three phosphates. Energy provided by ATP is used in active transport to contract muscles to make proteins and in many other ways.
A Chemical reactions proceed more quickly at higher temperatures. What is ATP and its function. The Cori cycle costs net 4 ATP loss because i _____ glycolysis produces 2 ATP whereas production of ii _____ uses 6 ATP.
Transport workATP supplies the. Up to 24 cash back There are a total of three 3 main types of cellular work specifically ran by adenosine triphosphate or ATP. ATP-Driven Work Cells need energy to grow reproduce and maintain homeostasis but for the energy provided by ATP to be useful it must be coupled with work.
ATP functions as the energy currency for cells. As ATP is used for energy a phosphate group or two are detached and either ADP or AMP is produced. Chemical Work- Converts polymers to monomersfor example a cell creating more molecules.
The Adenosine triphosphate ATP molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the molecular currency of intracellular energy transfer. 85Which of the following does not describe uses for the ATP molecule. So when a cell needs energy it disrupts this bond to form adenosine diphosphate ADP and along with it a free phosphate molecule.
You eat food which gives you energy in the form of ATP then you cells will break down the ATP into ADP to get energy for themselves by breaking one of the bonds in phosphate groups then the. These processes as well as others create a high demand for ATP. Legs move pedals of bike.
C Larger particles move faster than smaller ones and thus collide more frequently and more forcefully. What are the 3 types of work the energy uses called. The business end of ATP which contains 3 phosphate groups.
ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate and is a very important molecule found in cells. The contraction of a muscle. Enzymes work by raising the energy of activation.
ATP Adenosine triphosphate consists of three phosphate groups and within these phosphate groups the high-energy bonds are present. ATP is consumed for energy in processes including ion transport muscle contraction nerve impulse propagation substrate phosphorylation and chemical synthesis. In contrast the Cahill cycle causes loss of 4 additional ATP because excess ATP is needed in liver to process nitrogen for the formation of iii_____.
ATP has three phosphate groups and there is a high-energy bond in between the phosphates. ATP Adenosine triphosphate consists of three phosphate groups and within these phosphate groups the high-energy bonds are present. The structure of ATP is that of an RNA nucleotide with three phosphates attached.
ATP Adenosine triphosphate consists of three phosphate groups and within these phosphate groups the high-energy bonds are present. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. Three types of Cellular Work.
In each case ATP hydrolysis leads to a change in a proteins chape and often its ability to bind another molecule This change may occur via a phosphorylated intermediate In most examples of mechanical work involving motor proteins walking on cytoskeletal elements a. 85 A transport across membranes B pigment structure C mechanical work D chemical work. A chemical work B mechanical work C transport across membranes D pigment structure Answer.
- Beating of a cilium - Movement of chromosomes during cell replication Transport Work. That is ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. D Catalysts increase the rate of chemical reactions.
Mechanical transport and chemical work in the cell nearly always powered by the hydrolysis of ATP. - Pumping of protons against a concentration gradient across a cell membrane - Active transport of K and Na ions across a cell membrane Chemical Work. Chemical mechanical and transport work.
The energy from ATP is used to do _____ types of work. Chemical workATP supplies the energy needed to synthesize the macromolecules that comprise the cell. A DNA is a long double-stranded molecule made up of A T G and C bases.
- Synthesis of DNA from nucleotide components - Linking of amino acids to form a protein. What kind of work do cells do. Which of the following does NOT describe enzymes.
Which of the following does not describe uses for the ATP molecule. ATP plays a very important role in preserving the structure of the cell by helping the assembly of the cytoskeletal elements. Chemical work mechanical work and transport work Figure 7-10.
B Chemical reactions progress at a faster rate when the reacting particles are present in higher numbers. To provide energy for cellular processes. The second and third phosphate bounds often store lots of energy which can be used to power chemical reactions in the human body.
A pigment structure B transport across membranes C chemical work D mechanical work. ATP which stands for adenosine. There are at least three distinct uses for ATP in cells.
Amechanical work Bchemical work Cpigment structure Dtransport across membranes 85 C pigment structure. It allows the cell to store energy briefly and transport it within the cell to support endergonic chemical reactions. Negatively charged phosphate groups lead to stored potential energy.
Mechanical Work-Contraction of muscle for example beating of cilia muscle contractions etc or any part of the cell generating movement. In a cell this work takes three main forms. Mechanical Chemical Radiant Electrical.

System Boundary For The Life Cycle Assessment Considered In This Study Download Scientific Diagram
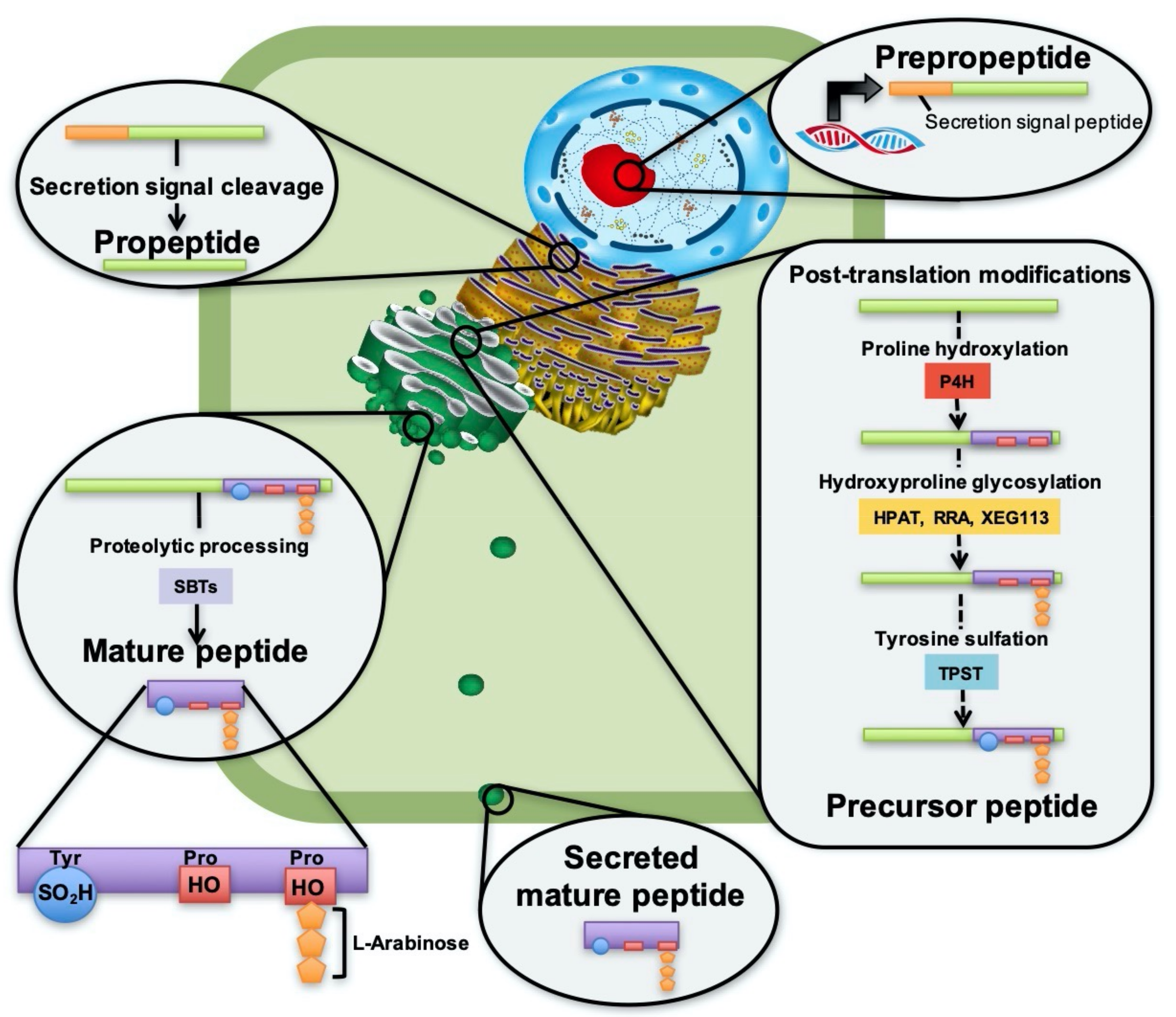
Genes Free Full Text The Psy Peptide Family Expression Modification And Physiological Implications Html
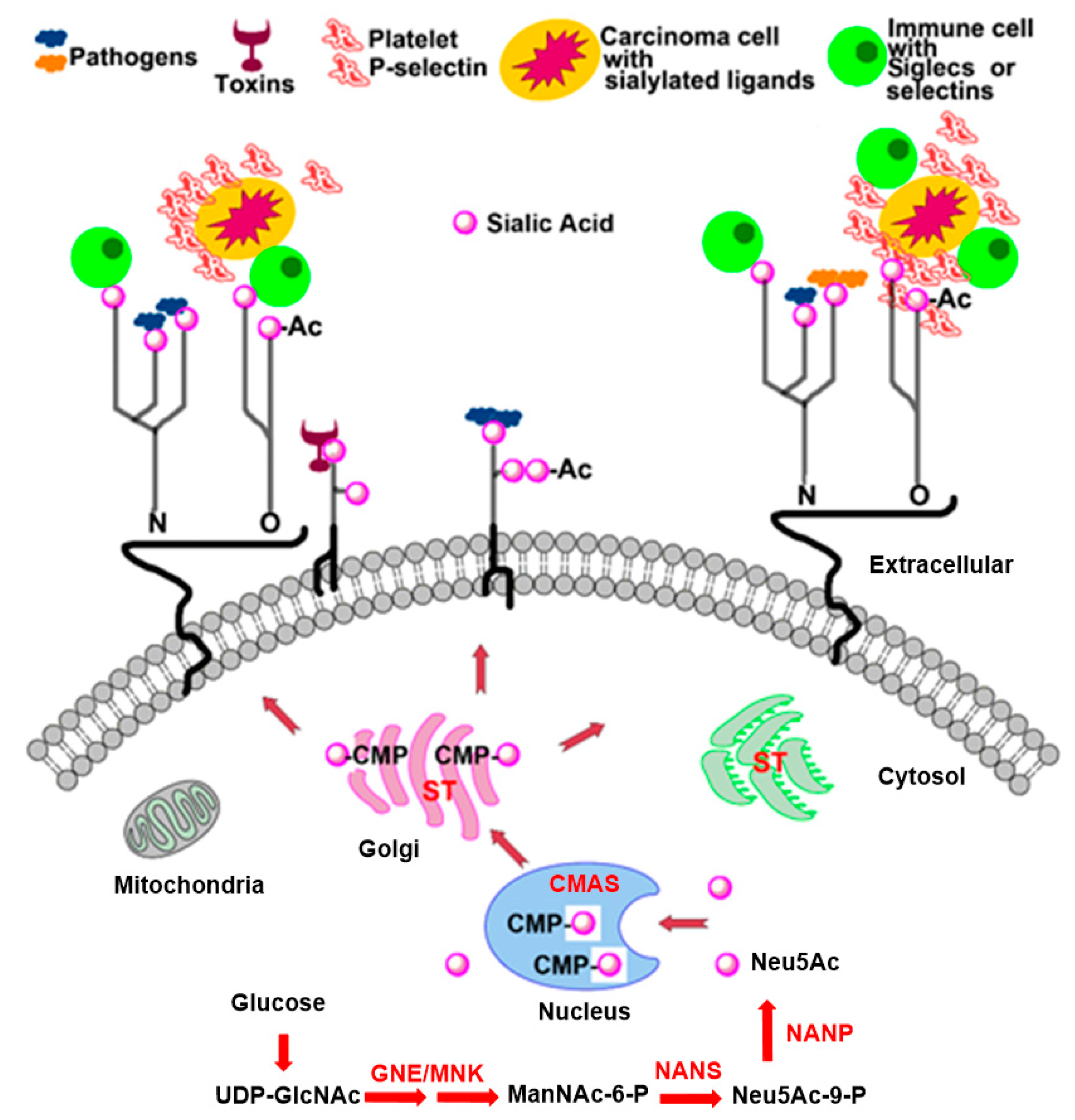
Molecules Free Full Text Sialyltransferase Inhibitors For The Treatment Of Cancer Metastasis Current Challenges And Future Perspectives Html
Ros Responsive Drug Ddss A Ros Generation Based On Photodynamic Download Scientific Diagram
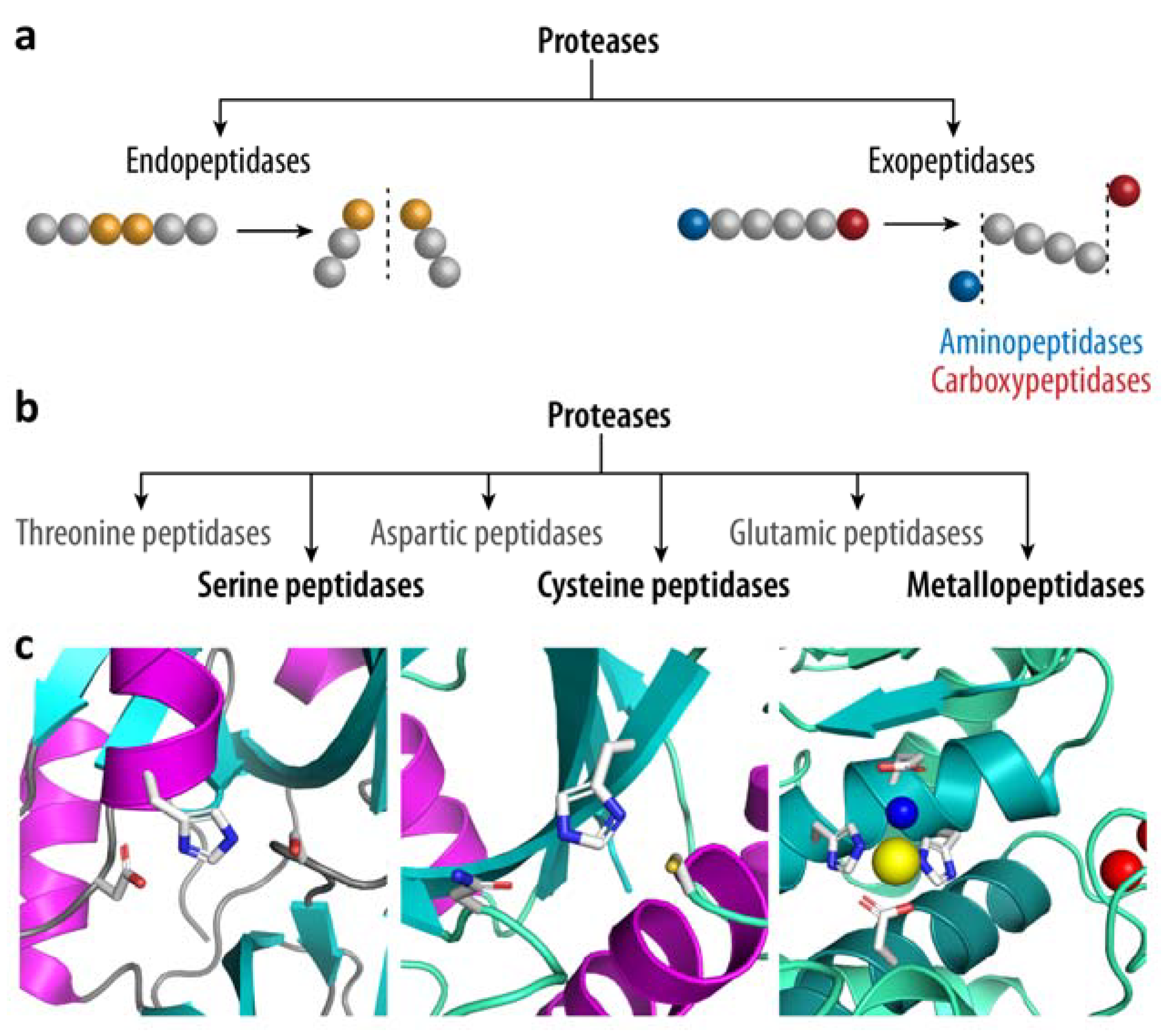
Biomolecules Free Full Text An Introduction To Bacterial Biofilms And Their Proteases And Their Roles In Host Infection And Immune Evasion Html

Difference Between Stomata Of Monocot And Dicot Plants Definition Guard Cells Distribution Of Stomata Study Biology Ground Tissue Irregular Patterns

Muscle Cell News Musclecellnews Twitter

The Hydrolysis Mechanism Of A Gh45 Cellulase And Its Potential Relation To Lytic Transglycosylase And Expansin Function Journal Of Biological Chemistry

Cell Swelling By Energy Depletion The Na K Atpase Maintains A Low Download Scientific Diagram
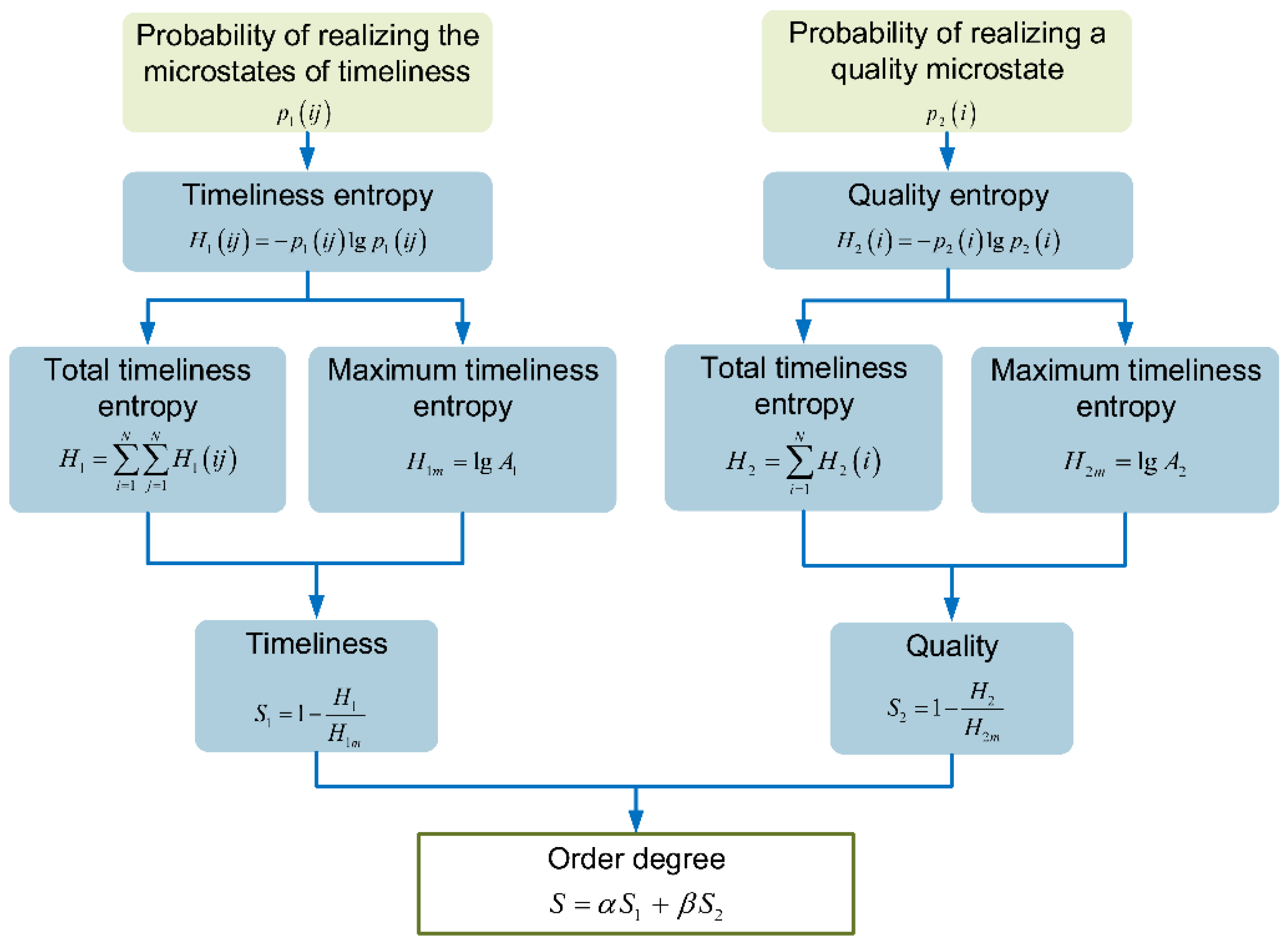
Entropy Free Full Text Influences Of Different Architectures On The Thermodynamic Performance And Network Structure Of Aircraft Environmental Control System Html
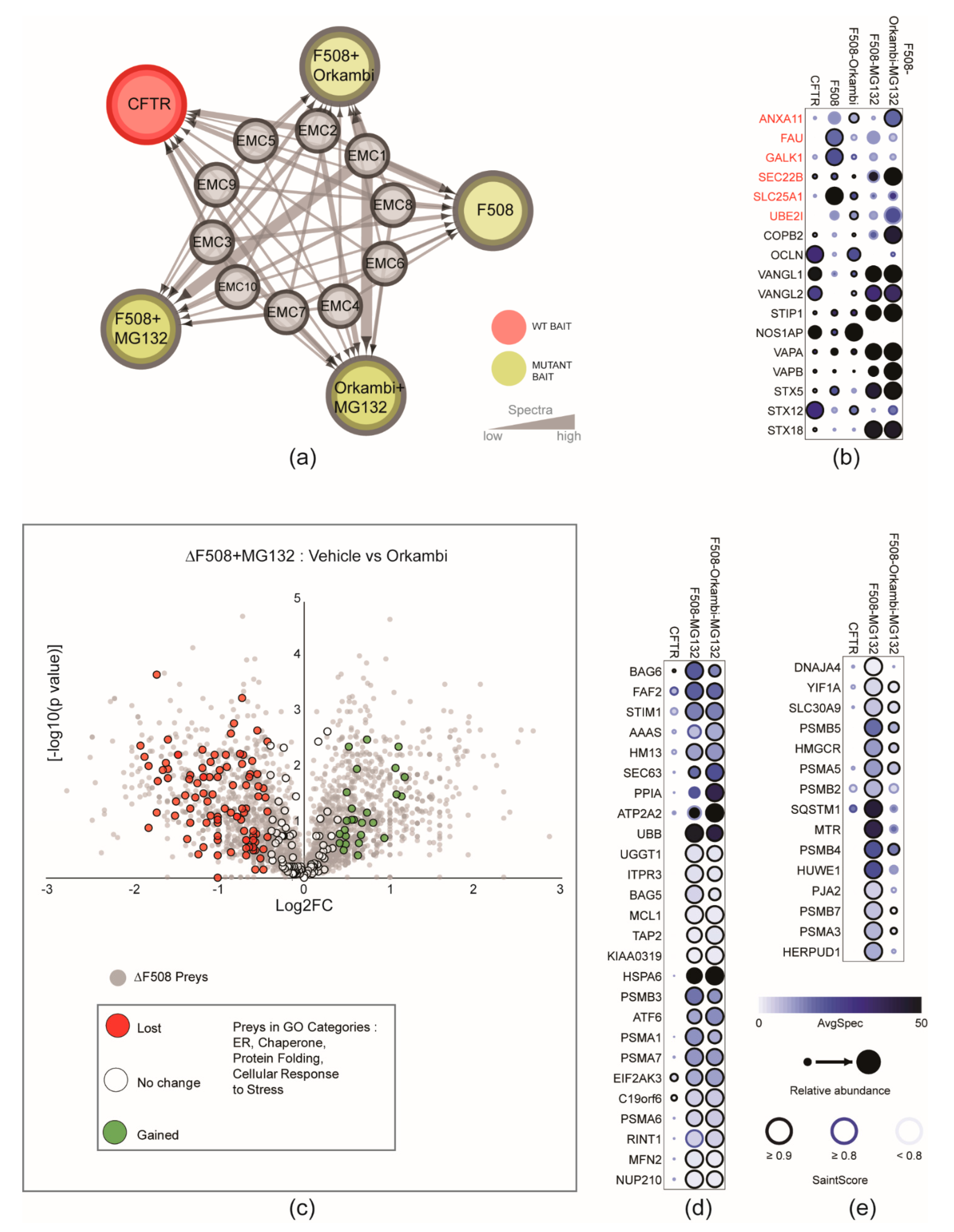
Ijms Free Full Text Proximity Profiling Of The Cftr Interaction Landscape In Response To Orkambi Html
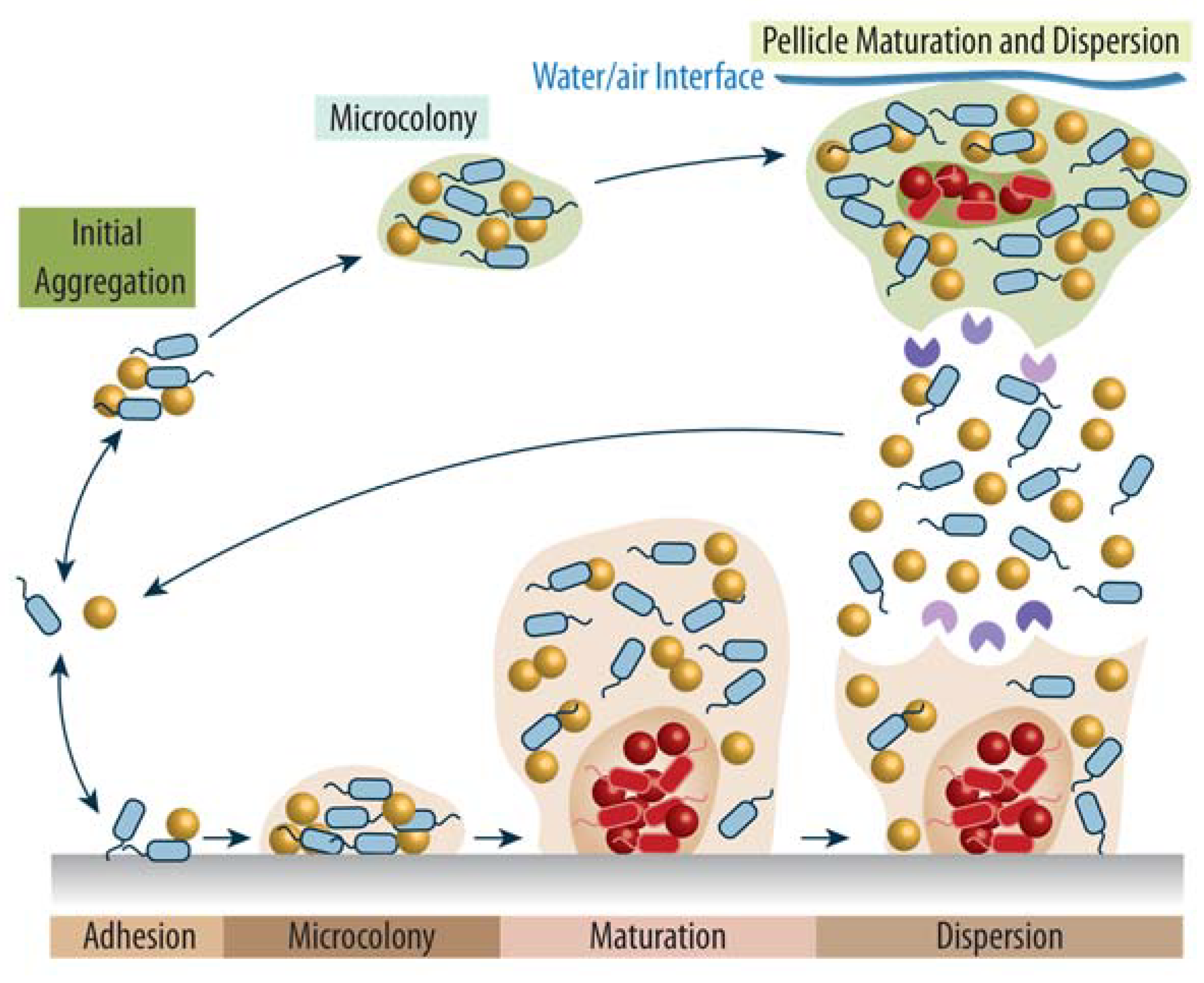
Biomolecules Free Full Text An Introduction To Bacterial Biofilms And Their Proteases And Their Roles In Host Infection And Immune Evasion Html
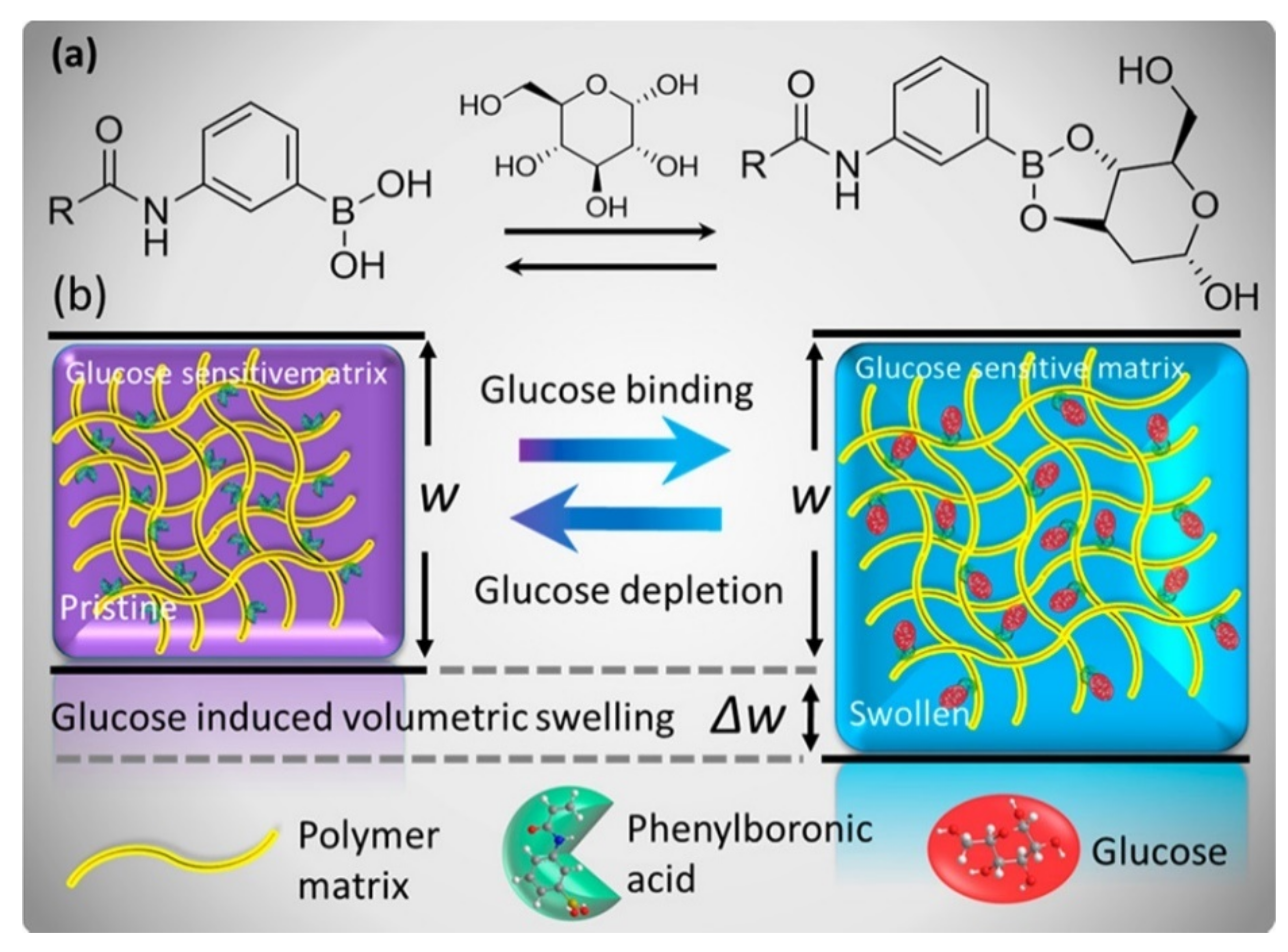
Polymers Free Full Text Shaping Macromolecules For Sensing Applications Mdash From Polymer Hydrogels To Foldamers Html

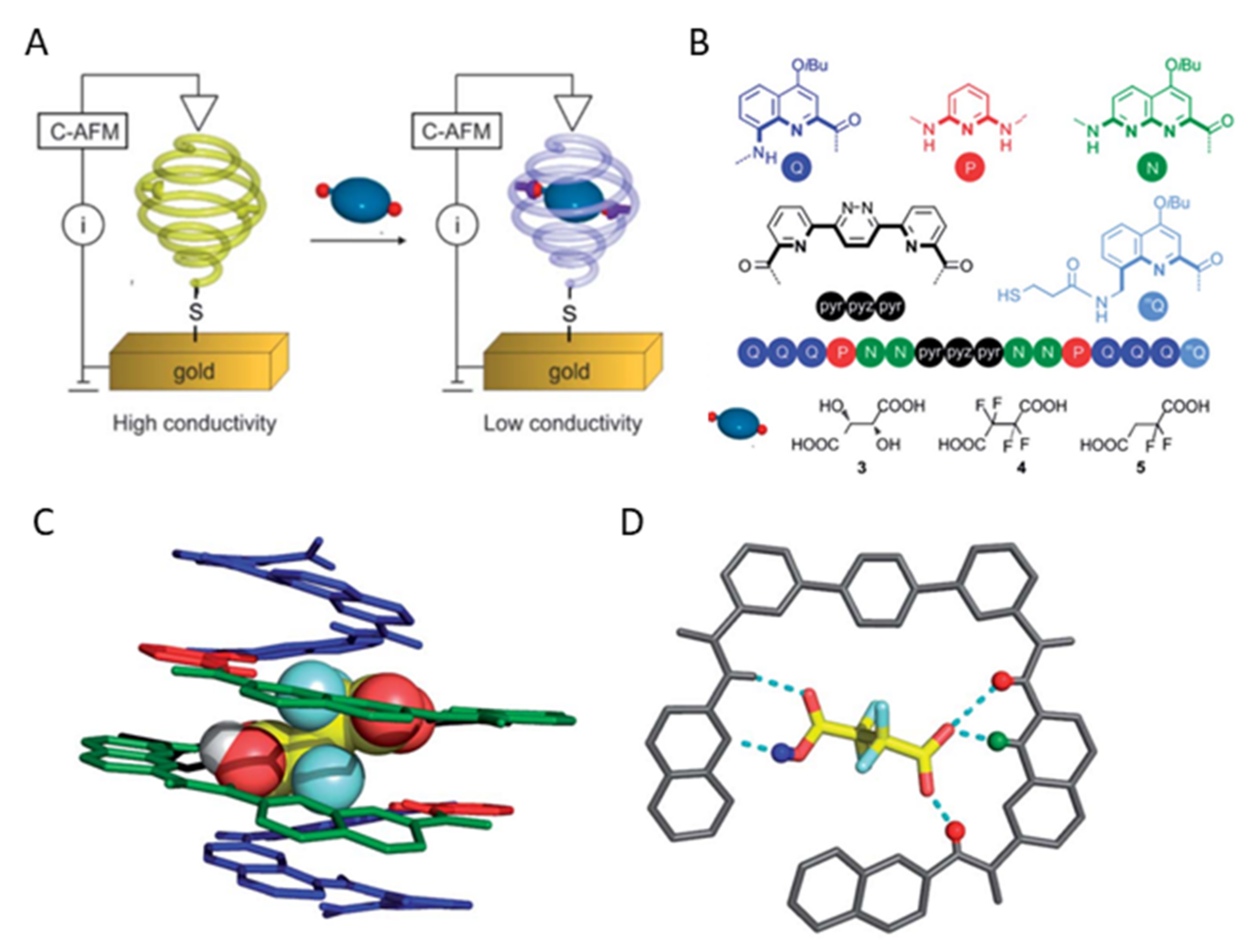
Polymers Free Full Text Shaping Macromolecules For Sensing Applications Mdash From Polymer Hydrogels To Foldamers Html

The Many Mechanisms By Which Hyperglycemia May Feed Cancer Cells Download Scientific Diagram
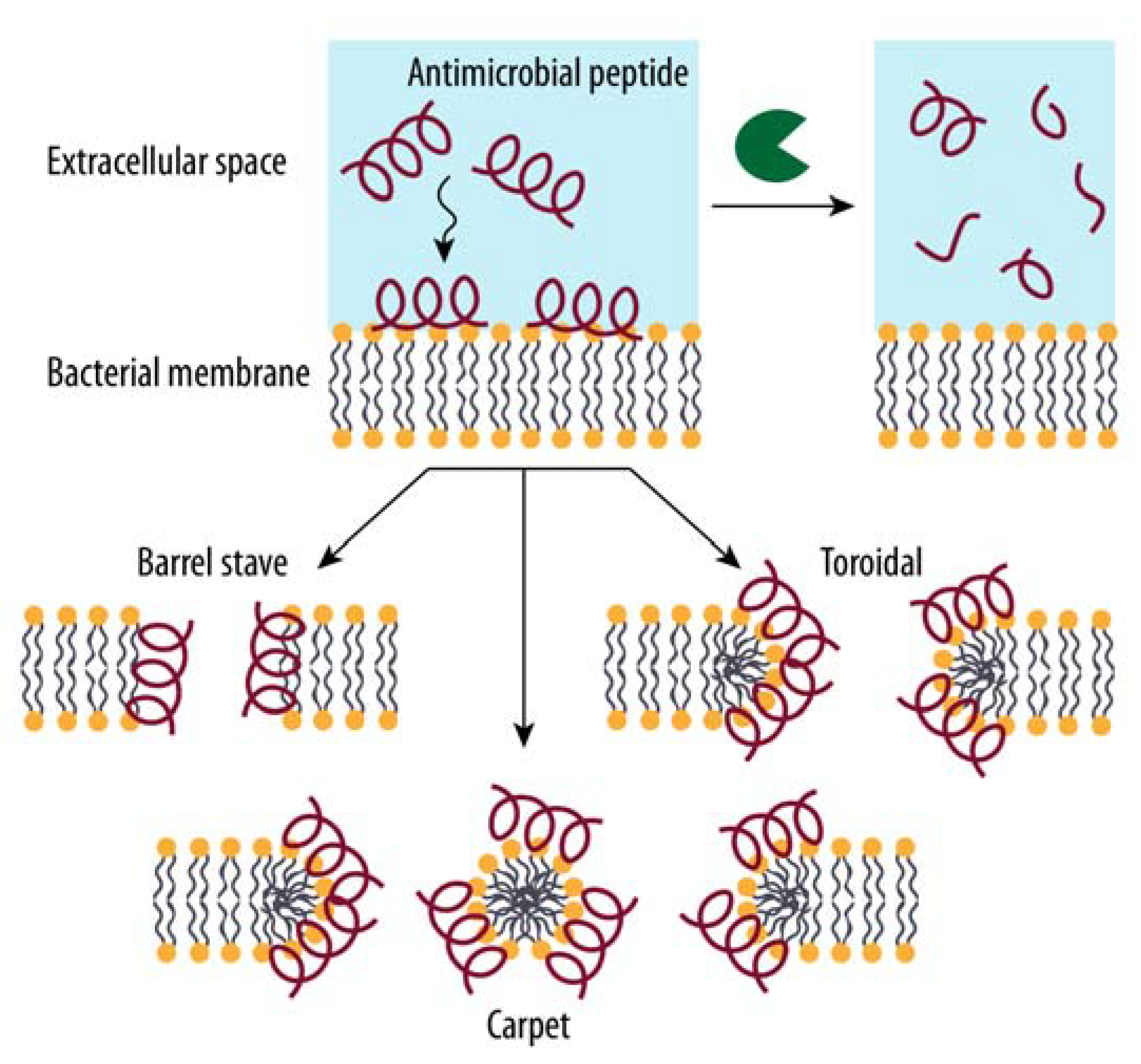
Biomolecules Free Full Text An Introduction To Bacterial Biofilms And Their Proteases And Their Roles In Host Infection And Immune Evasion Html
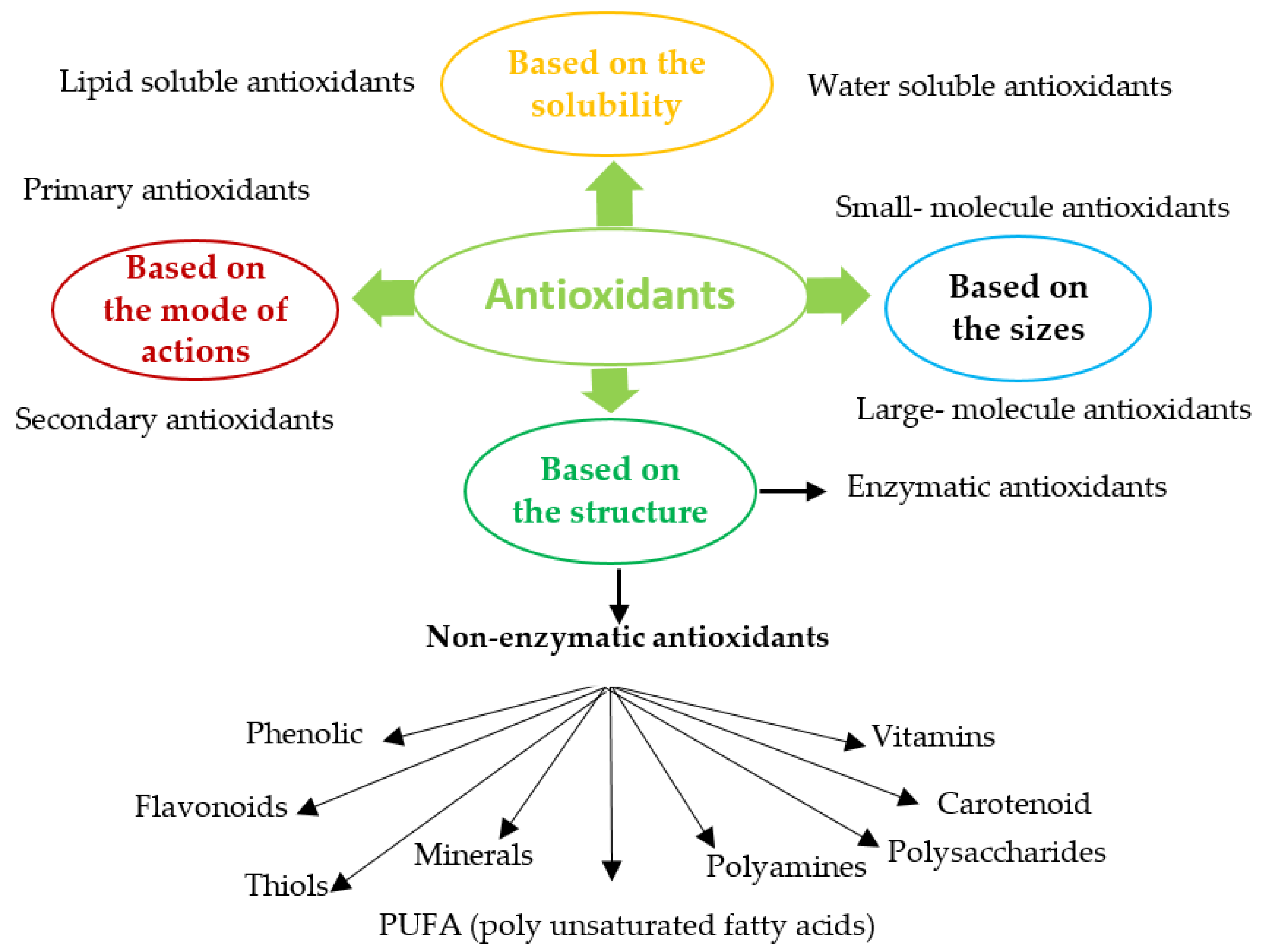
Applied Sciences Free Full Text Antioxidant Production In Dunaliella Html

In The Molecule Below What Are The Hybridizations Of C1 C2 C3 And C4 Respectively A Sp Sp Sp2 Sp2 B With Images This Or That Questions Question Of The Day
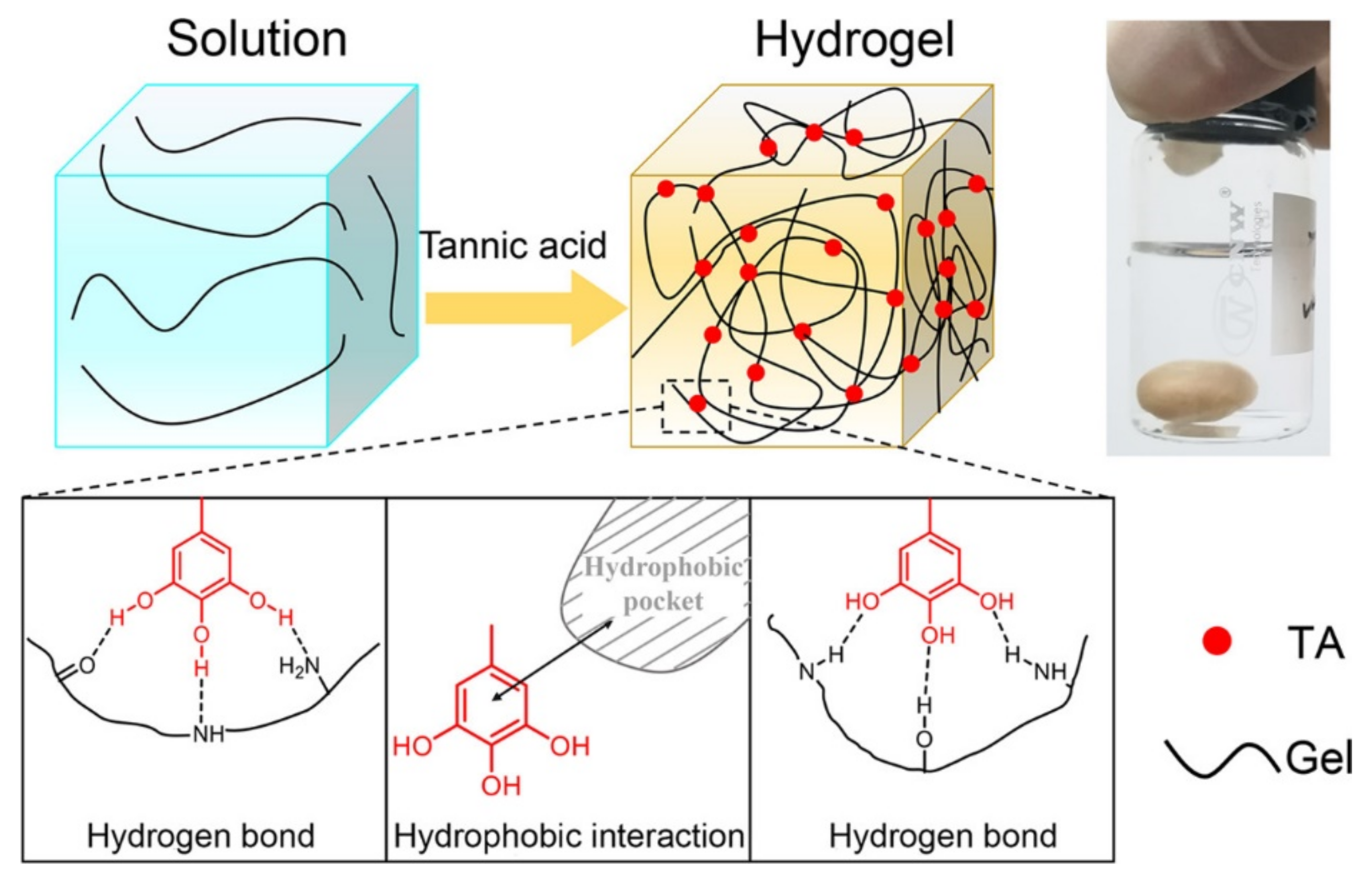
Polymers Free Full Text Shaping Macromolecules For Sensing Applications Mdash From Polymer Hydrogels To Foldamers Html
Comments
Post a Comment